Public Health Planning Process and Evaluation: A Comprehensive Guide
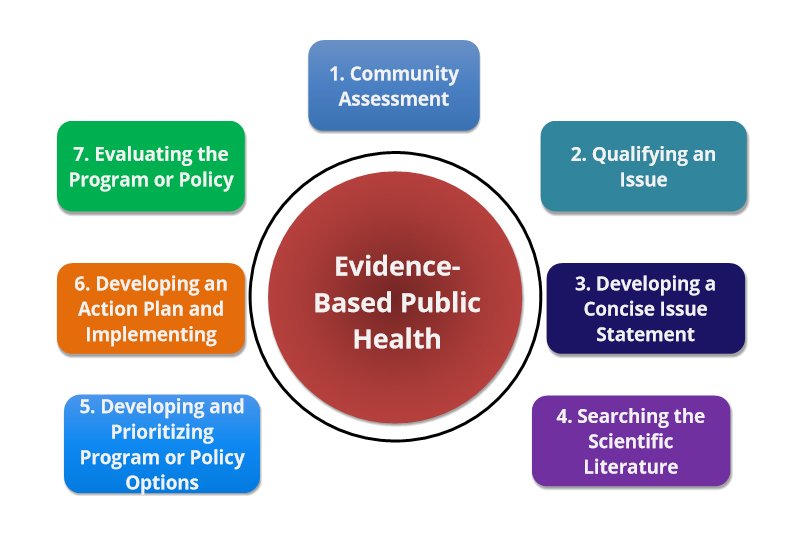
Public health planning is an essential component of public health practice. It involves the systematic development, implementation, and evaluation of policies, programs, and interventions aimed at improving the health of populations. Effective planning requires a comprehensive approach that takes into account the needs of the community, available resources, and the latest scientific evidence. In this article, we will discuss the public health planning process and evaluation, including the key steps involved and the best practices for each.
Step 1: Define the problem and assess the needs
The first step in the public health planning process is to define the problem and assess the needs of the community. This involves identifying the health issue that needs to be addressed, the populations affected, and the underlying causes of the problem. To do this, public health planners often rely on data from various sources, such as health surveys, disease registries, and epidemiological studies.
Once the problem has been defined, the next step is to assess the needs of the community. This involves identifying the resources and services currently available, as well as any gaps or deficiencies in the system. Community input is also essential at this stage, as it helps to ensure that the planning process is tailored to the specific needs and priorities of the community.
Step 2: Develop goals and objectives
The next step in the public health planning process is to develop goals and objectives for the intervention. Goals are broad statements that describe the overall aim of the intervention, while objectives are specific, measurable targets that the intervention is intended to achieve. Goals and objectives should be based on the needs assessment and should be realistic and achievable given the available resources.
Step 3: Develop an intervention
Once the goals and objectives have been established, the next step is to develop an intervention. This involves selecting the most appropriate strategies and interventions to achieve the desired outcomes. Strategies may include policy changes, education campaigns, or community-based interventions.
When selecting interventions, it is important to consider their effectiveness, feasibility, and sustainability. The most effective interventions are evidence-based, meaning that they are supported by scientific research. Feasibility refers to the practicality of implementing the intervention, while sustainability refers to the long-term viability of the intervention.
Step 4: Implement the intervention
The next step in the public health planning process is to implement the intervention. This involves putting the plan into action and monitoring its progress. Implementation requires careful coordination of resources, including personnel, funding, and equipment. It is also important to engage with stakeholders, including community members, to ensure that the intervention is well-received and effective.
Step 5: Evaluate the intervention
The final step in the public health planning process is to evaluate the intervention. Evaluation involves assessing the effectiveness, efficiency, and impact of the intervention. This helps to determine whether the intervention achieved its intended outcomes and whether any modifications are necessary to improve its effectiveness.
Evaluation can take many forms, including process evaluation, which assesses the implementation of the intervention; impact evaluation, which measures the effects of the intervention on health outcomes; and cost-effectiveness analysis, which assesses the costs and benefits of the intervention.
- How to Write the Common App Essay -Tips and Tricks
- Nurse Practitioner Professional Career Planner
- Capella Flexpath Assessments Answer
Best practices for public health planning and evaluation
Effective public health planning and evaluation require a range of skills and competencies. Here are some best practices for each step of the process:
Needs assessment: Use a variety of data sources to obtain a comprehensive picture of the health issue and community needs.
Goal setting: Ensure that goals and objectives are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Intervention selection: Use evidence-based interventions that are feasible and sustainable.
Implementation: Ensure that the intervention is well-coordinated and engages stakeholders, including community members.
Evaluation: Use rigorous evaluation methods to assess the effectiveness, efficiency, and impact of the intervention.
Conclusion
Public health planning and evaluation are crucial components of public health practice. By following a systematic process that involves defining the problem, assessing needs, developing goals and objectives, implementing the intervention, and evaluating its effectiveness, public health practitioners can develop effective and evidence-based interventions that improve the health of communities. Best practices for each step of the process include using a variety of data sources for needs assessment, setting SMART goals and objectives, selecting evidence-based interventions, ensuring coordinated implementation, and using rigorous evaluation methods to assess impact. By following these best practices, public health practitioners can maximize the impact of their interventions and improve the health outcomes of the communities they serve.
Find online help in writing essays, research papers, term papers, reports, movie reviews, annotated bibliographies, speeches/presentations, projects, presentations, dissertation services, theses, research proposals, essay editing, proofreading, Book reviews, article reviews, formatting, personal statements, admission essays, scholarship essays, application papers, among others.


 WRITE MY ESSAY NOW!
WRITE MY ESSAY NOW!