Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic respiratory condition that causes airflow obstruction, making it difficult to breathe. COPD can lead to several complications, including pneumonia. Pneumonia is an infection that affects the lungs and can be life-threatening, especially in people with COPD. In this article, we will discuss the risks associated with COPD and pneumonia.
What is COPD?
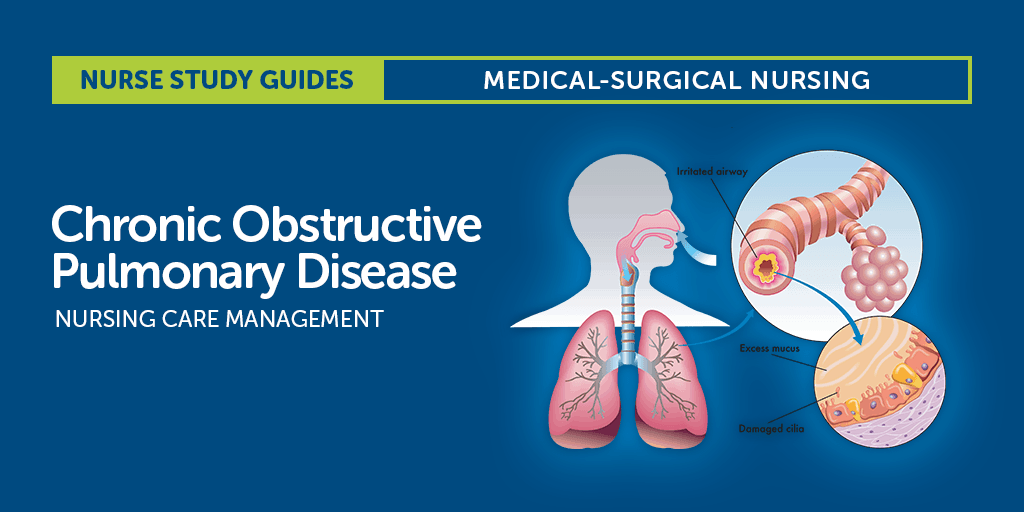
COPD is a chronic lung disease that causes difficulty in breathing. COPD is a combination of two lung conditions: chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Chronic bronchitis is inflammation of the airways in the lungs, while emphysema is damage to the air sacs in the lungs, which makes it difficult to exhale.
COPD is most commonly caused by smoking, although exposure to other lung irritants such as air pollution, chemical fumes, and dust can also contribute to the development of the condition. Symptoms of COPD include coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and excess mucus production.
COPD is a progressive disease, which means that the symptoms gradually worsen over time. There is no cure for COPD, but treatment can help manage symptoms and slow down the progression of the disease. Treatment options for COPD include medication, oxygen therapy, pulmonary rehabilitation, and surgery.
What is Pneumonia?
Pneumonia is an infection that affects the lungs. The infection can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other microorganisms. Pneumonia can affect anyone, but it is most dangerous for young children, the elderly, and people with weakened immune systems.
Pneumonia can cause inflammation in the air sacs in the lungs, making it difficult to breathe. Symptoms of pneumonia include cough, fever, chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, and confusion.
Pneumonia is a serious condition and can be life-threatening, especially for people with pre-existing respiratory conditions such as COPD. Treatment for pneumonia usually involves antibiotics, rest, and plenty of fluids. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary.
Risks of COPD and Pneumonia
People with COPD are at an increased risk of developing pneumonia. This is because COPD damages the lungs and weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections. The risk of developing pneumonia is also higher for people with COPD who smoke, have frequent exacerbations, and are over the age of 65.
Pneumonia can cause complications in people with COPD, including respiratory failure, sepsis, and even death. The risk of complications is higher for people with severe COPD and those who have other underlying health conditions such as heart disease and diabetes.
Prevention
Preventing pneumonia is important for people with COPD. There are several steps that people with COPD can take to reduce their risk of developing pneumonia:
- Get vaccinated: Vaccines can help prevent pneumonia. The pneumococcal vaccine can protect against the most common types of bacteria that cause pneumonia. The flu vaccine can also help prevent respiratory infections that can lead to pneumonia.
- Practice good hygiene: Washing hands regularly and avoiding contact with people who are sick can help prevent the spread of respiratory infections.
- Quit smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for COPD and pneumonia. Quitting smoking can help reduce the risk of developing these conditions.
- Manage COPD symptoms: Managing COPD symptoms can help prevent exacerbations, which can increase the risk of developing pneumonia. Treatment options for COPD include medication, oxygen therapy, pulmonary rehabilitation, and surgery.
Treatment
Treating pneumonia in people with COPD can be challenging, as the infection can make it difficult to breathe. Treatment for pneumonia in people with COPD typically involves antibiotics and oxygen therapy. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary.
Antibiotics: Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial pneumonia. The choice of antibiotic depends on the type of bacteria causing the infection. It is important to take the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if the symptoms improve.
Oxygen Therapy: Oxygen therapy may be necessary to help people with COPD and pneumonia breathe easier. Oxygen can be delivered through a nasal cannula, face mask, or other devices. Oxygen therapy can help improve oxygen levels in the blood and reduce the workload on the lungs.
Hospitalization: Hospitalization may be necessary for people with severe pneumonia and COPD. In the hospital, the person will receive oxygen therapy, intravenous antibiotics, and other treatments as necessary. In severe cases, a ventilator may be necessary to help the person breathe.
Preventing Exacerbations
Exacerbations, also known as flare-ups, are episodes where COPD symptoms worsen. Exacerbations can increase the risk of developing pneumonia in people with COPD. Preventing exacerbations is an important part of managing COPD.
Some ways to prevent exacerbations include:
- Taking medications as prescribed: Taking medications as prescribed can help prevent exacerbations and manage symptoms.
- Avoiding triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers that can worsen COPD symptoms, such as air pollution and allergens.
- Staying active: Regular exercise can help improve lung function and reduce the risk of exacerbations.
- Getting regular check-ups: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help identify and treat exacerbations early.
Conclusion
In conclusion, people with COPD are at an increased risk of developing pneumonia. Pneumonia can cause complications in people with COPD, including respiratory failure, sepsis, and even death. Preventing pneumonia and exacerbations is an important part of managing COPD. Vaccines, good hygiene practices, quitting smoking, managing COPD symptoms, and staying active can all help reduce the risk of developing pneumonia in people with COPD. Early identification and treatment of exacerbations can also help prevent complications such as pneumonia. If you have COPD, it is important to work with your healthcare provider to develop a plan to manage your symptoms and reduce the risk of developing pneumonia.
- What Is Respiratory Acidosis: Types, Symptoms, Causes and More
- What is kidney cancer? Symptoms, Signs, Causes & Treatment
- What Is Erectile Dysfunction (ED) and How to Treat It
- What Are the Different Types of Strokes? Causes, Symptoms & Treatments
- Everything You Need to Know About Pneumonia: Causes & Treatment
Find online help in writing essays, research papers, term papers, reports, movie reviews, annotated bibliographies, speeches/presentations, projects, presentations, dissertation services, theses, research proposals, essay editing, proofreading, Book reviews, article reviews, formatting, personal statements, admission essays, scholarship essays, application papers, among others.


 WRITE MY ESSAY NOW!
WRITE MY ESSAY NOW!